 This article is part of the Teach IELTS series at IELTS Academic, an online provider of skills training for IELTS and English as a foreign language.
This article is part of the Teach IELTS series at IELTS Academic, an online provider of skills training for IELTS and English as a foreign language.
Spelling, distractors, paraphrase, and different English accents are all common problems faced by candidates in the IELTS Listening module. These ten IELTS Listening teaching tips should help both new and experienced IELTS teachers get the best out of their students.
IELTS Listening is a paper-based test of 40 questions that takes around 40 minutes to complete. Candidates hear four passages in total and answer ten questions about each. The passages, or sections, follow a set order:
- Section 1: A conversation on an everyday topic
- Section 2: A monologue on an everyday topic
- Section 3: A conversation on an academic topic
- Section 4: A monologue on an academic topic
The Listening test is the same in both the General Training and Academic modules of IELTS. Speakers may use a range of accents and varieties of English.
While listening, candidates must read and answer a variety of question types. There are short interludes before and during each passage to allow candidates to read the questions in advance. Analysis of the questions therefore forms a major part of any IELTS Listening strategy.
After all four passages have been played, candidates have a further 10 minutes to transfer their answers to an answer sheet. At this point, poor spelling can seriously affect a candidate’s score.
As you can see, there are some important skills that need to be worked on in order to raise students’ listening scores. Read on for some practical classroom tips on how to teach IELTS Listening.
Looking for a basic guide to IELTS Listening? Read this first: IELTS Listening: Introduction
Completely new to teaching IELTS? Read this first: How to Teach IELTS: The Basics
1. Set realistic goals
In order to achieve a good score of IELTS 7.0, your students need to answer 30 out of 40 questions correctly. You should really drum this point into them. Why? It means they can quickly recover from any answers they miss and focus all their attention on the next question. Lead them out of the perfectionist mindset and get them thinking more pragmatically about what constitutes a good performance in the test.
2. Analyse the questions together
This is a controversial point, but I always like to give my students much more time to read the questions than they will receive in the real IELTS Listening test. First, I allow them to read through all ten questions at their leisure. I don’t want them distracted while we’re discussing a particular question. The we analyse each question for information type, troubleshooting, and grammatical clues. Later on students can be pushed to perform similar analysis under much more time pressure.
3. Predict possible answers
As well as analyse the questions, students should be encouraged to predict answers. Predicting is not the same as guessing, since you’re not asking them to write down their prediction. What prediction does is reveal if students have properly analysed the question for content and grammatical form. Thus, it’s a great complement to the previous tip.
4. Practice targetted listening
I like to use this analogy with my students: imagine you arrived at the airport one hour ago for a flight that departs soon. Now recall what all the announcements in the past hour have said. Of course you can’t, because we only listen for information relevant to our own flight. That’s the essence of targetted listening: having a goal in terms of what information we want to receive. It follows naturally from proper analysis of the ten questions.
5. Accent exposure
Unlike in TOEFL, candidates in the IELTS test can expect to hear a variety of accents, from regional British accents to North American and Southern Hemisphere accents such as Australian and South African English. It’s a curious footnote to the history of IELTS, which began as ELTS but gained its initial ‘I’ when more English-speaking countries were invited to recognise the test for immigration purposes. If you’re not a natural show-off who enjoys flipping between accents in class, there’s a comparison of different English accents here.
6. Drill spellings
IELTS candidates are expected to be able to spell answers correctly. However, English allows for multiple spellings of names, so you can expect these words to be spelled out, e.g. I.E.L.T.S. This is most likely to happen in IELTS Listening Section 1 where filling out personal details is a common question type. Drill spellings multiple times, paying special attention to the errors that are most common for your language group. The letter ‘W’ is notoriously problematic as it’s easily confused with the ‘double-X’ modifier in spelling.
7. Drill numbers
Just like for numbers above, IELTS candidates can expect to write several numbers, including at least one long number such as a product code or phone number. The good news is that numbers require little in the way of comprehension. Concentration is key, along with anticipating the number in the first place.
8. Listen for corrections
Among the many distractors that test-writers incorporate, one of the most common is to have the speaker correct a previous statement, especially if it’s a spelling or number. Therefore, students should write down the final version that they hear, not the first. Add a bit of variation to your spelling and number drills by introducing corrections.
9. Self-correct for spelling and grammar
Students should be given some time after the recording to check their answers for spelling and grammar. Allow generous time for this stage and walk around the classroom, calling out question numbers where you can see that students have made mistakes. Give them the satisfaction of correcting their own mistakes before you do it for them.
10. Model good listening
Don’t just tell your students the correct answers. Walk them through the recording one more time, pausing at the critical moments to explain how each answer is given. The difference between a mediocre IELTS teacher and an outstanding one is that the best teachers are active and alert during listening passages for signs that reveal where their students are struggling.
Find more IELTS Listening techniques at IELTS Listening Tips: How to Improve Your Score.
Stuck for listening practice ideas? Try these IELTS Listening tests based on TED talks.
 This article is part of the Teach IELTS series at IELTS Academic, an online provider of skills training for IELTS and English as a foreign language.
This article is part of the Teach IELTS series at IELTS Academic, an online provider of skills training for IELTS and English as a foreign language.





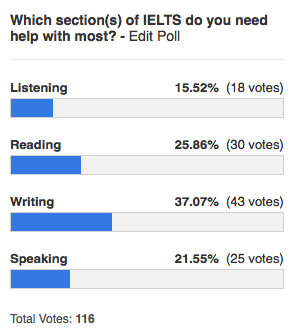 IELTS scores range from 0 to 9 and most students will be aiming for a score of 5 to 7. Universities often set requirements for each of the four sections, and students will often want to focus on one or two sections in particular. This poll conducted by IELTS Academic shows the kind of help students want most.
IELTS scores range from 0 to 9 and most students will be aiming for a score of 5 to 7. Universities often set requirements for each of the four sections, and students will often want to focus on one or two sections in particular. This poll conducted by IELTS Academic shows the kind of help students want most.



 Focus on IELTS has long been a popular choice for teachers and it’s easy to see why. There’s a good balance between authentic Academic IELTS test items and meaningful group exercises, while the inclusion of a grammar reference guide and extra writing practice make this a solid friend for classroom use. The new edition corrects most of the mistakes in the first edition and adds more EAP elements such as critical thinking and reflective learning. One remaining drawback is the lack of a version with full answer key and scripts. Also available in a Foundation edition that introduces test practice more gradually. Rating 9/10
Focus on IELTS has long been a popular choice for teachers and it’s easy to see why. There’s a good balance between authentic Academic IELTS test items and meaningful group exercises, while the inclusion of a grammar reference guide and extra writing practice make this a solid friend for classroom use. The new edition corrects most of the mistakes in the first edition and adds more EAP elements such as critical thinking and reflective learning. One remaining drawback is the lack of a version with full answer key and scripts. Also available in a Foundation edition that introduces test practice more gradually. Rating 9/10 One unique aspect of the Objective series is that test practice exercises are mostly written to focus students’ attention on a particular item type. There’s also an attractive presentation, discussion-led format, and strong grammar coverage throughout both books. The inclusion of test items from both the Academic and General Training modules in both books can be either a blessing or a curse depending on your teaching situation. A self-study student’s book with answer key and scripts is available for a slightly higher price, and there’s a teacher’s book with regular practice tests. Be warned: the level of questions in Objective IELTS Advanced is extremely challenging. Rating 8/10
One unique aspect of the Objective series is that test practice exercises are mostly written to focus students’ attention on a particular item type. There’s also an attractive presentation, discussion-led format, and strong grammar coverage throughout both books. The inclusion of test items from both the Academic and General Training modules in both books can be either a blessing or a curse depending on your teaching situation. A self-study student’s book with answer key and scripts is available for a slightly higher price, and there’s a teacher’s book with regular practice tests. Be warned: the level of questions in Objective IELTS Advanced is extremely challenging. Rating 8/10
 At first glance this seems to be a supplement to Focus on IELTS, but it’s actually a radically different kind of coursebook, one very well suited to self-study. Test strategies are broken down into easy-to-follow processes, and authentic test items are supplemented with directions in blue text. There’s also a full answer key. The new edition of the book includes both audio CDs and is therefore an even more complete package than the first edition. The only drawback is that it’s a little too process-oriented for classroom situations. Rating 9/10
At first glance this seems to be a supplement to Focus on IELTS, but it’s actually a radically different kind of coursebook, one very well suited to self-study. Test strategies are broken down into easy-to-follow processes, and authentic test items are supplemented with directions in blue text. There’s also a full answer key. The new edition of the book includes both audio CDs and is therefore an even more complete package than the first edition. The only drawback is that it’s a little too process-oriented for classroom situations. Rating 9/10 Independent learners will appreciate these self-study guides from Cambridge which focus on grammar and vocabulary with an academic dimension. Suitable for all low- to high-intermediate-level students. Both books come with an audio CD, which means that test-takers are activating more than just their reading and writing skills. Of course, it is ideal if these books can be supplemented with opportunities for spoken output such as a group lesson or study buddy. Rating 8/10
Independent learners will appreciate these self-study guides from Cambridge which focus on grammar and vocabulary with an academic dimension. Suitable for all low- to high-intermediate-level students. Both books come with an audio CD, which means that test-takers are activating more than just their reading and writing skills. Of course, it is ideal if these books can be supplemented with opportunities for spoken output such as a group lesson or study buddy. Rating 8/10
